3D object를 2D에 적절한 size, position, orientation 표현하기 위해서는 Intrinsic/Extrinsic parameter를 알아야 한다. Calibration은 해당 parameter를 구하는 과정이다.
Camera lens system
1. Pinhole camera

2. Modified camera

| Focal length | Distance between lens and image plane |
| Principal point | Where optical axis meets image plane |
Camera paramter
1. Intrinsic

2. Extrinsic

카메라의 position과 orientation을 말한다.
Parameter는 항상 일정하지 않기 때문에 calibration을 통해서 알맞은 parameter를 찾아내서 사용해야 한다.
3D-2D projection
다음의 식을 이용해서 구할 수 있다.
q = MQ

q = sMWQ

Homography
planar projective transformation.

Unknown이 8개이므로 관련된 식이 8개 필요하다. Homography를 구하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
1. Get Homography using "q = HQ"
Sample point에 대해 다음의 식을 얻을 수 있다.

이를 통해서 sample point를 다음과 같이 정의할 수 있다.

이로써 sample point 1에 대해서 H와 관련된 식 2개를 얻을 수 있음을 알 수 있다. 따라서 unknown이 8개이므로 총 4개의 sample point를 가지고 있다면 homography를 구할 수 있게 된다. 위 식을 행렬식으로 변환하면 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.

정확히 4개의 point를 이용해서 homography를 구할 수 있다. 하지만, 현실에서는 이보다 많은 점을 이용해 homography를 구하게 된다. 오차가 있을 수 있기 때문이다.
2. Homography decomposition using "q = HQ = sMWQ"
내부 parameter를 구하기 위해서는 위에서 구한 homography를 intrinsic/extrinsic parameter로 분해해줘야 한다. "q=HQ=sMWQ"이므로 "H=sMW"이다.

[h1h2h3]=sM[r1r2t]
then we have
h1=sMr1,h2=sMr2,h3=sMt
r1=M−1sh1,r2=M−1sh2,t=M−1sh3
2-1. r1 and r2 are orthogonal
rT1r2=0
(M−1sh1)TM−1sh2=0
hT1(M−1)TM−1h2=0 ... (1)
2-2. |r1|=|r2|=1
M−1h1=M−1h2
hT1(M−1)TM−1h1=hT2(M−1)TM−1h2
hT1(M−1)TM−1h1−hT2(M−1)TM−1h2=0 ... (2)
2-3. Let B = (M−1)TM−1

B는 Intrinsic parameter에 관한 식으로 이루어져 있어 B를 알면 intrinsic parameter를 구할 수 있다. (M−1)TM−1을 전개해 보니, symmetric임을 알 수 있다. 따라서 B의 unknown은 6개가 된다. 그리고 위의 조건들로부터 얻은 식 2개((1), (2))를 정리하면 하나의 homography로부터 2개의 식을 얻을 수 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
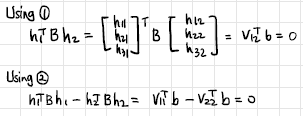
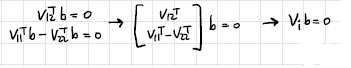
따라서 총 3개의 homography(=image)가 있으면 intrinsic parameter를 구할 수 있게 된다. 여기도 마찬가지로 실제로는 3개 이상의 image를 사용하게 된다.
Extrinsic parameter는 위에서 구한 r1,r2,r3=r1×r2,t를 통해서 구할 수 있다.
Camera Distortion
- Radial distortion
- Tangential distortion
Radial distortion
Lens가 spherical이어서 발생하는 문제이다. Taylor series를 이용해서 보상해준다.
xcorrected=x(1+k1r2+k2r4+k3r6+...)
ycorrected=y(1+k1r2+k2r4+k3r6+...)
일반적으로 k2까지 사용한다.
Tangential distortion
Lens와 CCD가 평행하지 않아서 발생하는 문제이다. p1,p2를 이용해서 보상해준다.
xcorrected=x+[2p1xy+p2(r2+2x2)]
ycorrected=y+[p1(r2+2y2)+2p2xy]
Distortion coefficients
xp=xd(1+k1r2+k2r4+k3r6)+[2p1xdyd+p2(r2+2x2d)]
yp=yd(1+k1r2+k2r4+k3r6)+[p1(r2+2y2d)+2p2xdyd]
Intrinsic parameter를 이용해서 xp와 yp를 구해서 unknown k1,k2,k3,p1,p2를 찾으면 된다. Unknown이 5개이므로 점 3개가 있으면 구할 수 있다.
*pinhole camera의 xp,yp

Calibration Procedure
- Homography for each images
- Camera prameter
- Distortion coefficient
- Repeat
- Get compensated point
- Update Parameter
- Get Distortion coefficient
Re-projection Error
ε=∑||p−q′||, q'=sMWQ
Augmented Reality
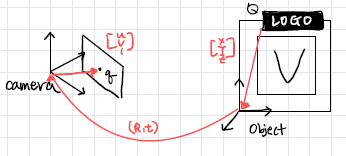
- Camera calibration
- Intrinsic parameter 구하기
- 다른 pose의 여러 이미지 사용
- Finding corner points of marker
- Estimation of Marker Pose
- marker의 position, orientation 찾기
- Finding homography
- Finding pose
- Projection to Image phase

'Study > Computer Vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 10. Deep Learning (0) | 2023.05.10 |
|---|---|
| 8. Homogeneous Transformation Matrix (0) | 2023.05.10 |
| 7. Fourier Descriptor (2) | 2023.05.10 |
| 6. Bayes Classifier (0) | 2023.05.10 |
| 5. Object Recognition (0) | 2023.05.10 |
